Why Glutamine is Important for Athletes | Recovery in Weight Training
Supplements are Essential at Better Progress
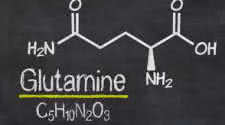
Of all the amino acids, glutamine (chemical symbol - Q) is one of the most abundant within skeletal muscle and throughout your body. While it exists naturally, it's also found in foods such as beef,
chicken, milk products, eggs, spinach, cabbage and beets. Glutamine is considered a conditionally essential amino acid - this means endogenous (internally produced) supply may not meet demands under
conditions of heavy metabolic stress like that experienced by bodybuilders engaged in rigorous training and/or dieting. Glutamine is also depleted by certain clinical conditions (e.g., stress,
injury states). Hence, glutamine depletion should be a concern for bodybuilders who commit their bodies to daily heavy physical stress, especially under conditions when trying to restrict calories,
as when dieting to get lean.
Skeletal muscle serves as the major storage pool for glutamine. As such, it's the main source for a number of processes and serves many areas of your body that require glutamine for normal function.
The production of several peptides, proteins, nucleotides and even glucose rely on glutamine. Of relevance, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is produced through the break-down of glutamine. GABA can
stimulate the production of growth hormone (GH), thus promoting fat metabolism and increased muscularity.
Alpha-ketogluterate (AKG) is produced from the conversion of glutamine and has been implicated in steroid biosynthesis. The gastrointestinal tract even needs glutamine to break down the foods you eat.
Other glutamine-hungry areas include the brain and the immune system. In fact, lymphocytes, macrophages and fibroblasts all use glutamine in energy production.
GLUTAMINE'S KEY BENEFITS
Glutamine is widely used by bodybuilders because it directly and indirectly boosts performance in a number of key areas. The physical demand of repetitive resistance-training sessions can deplete glutamine stores and lead to a number of problems in both general health and muscular development Recent research has shown that glutamine supplementation can:» Serve as a potent anti-catabolic factor and muscle-building aid during heavy training.
» Enhance cell volumization, which directly augments muscle "fullness" and turns on anabolic machinery.
» Increase leucine concentration and maintain a positive nitrogen balance in skeletal muscle, which is fundamental for muscle anabolism.
» Aid in lipolysis (fat-burning).
» Support growth hormone (GH) production (and is integral in the production of steroid hormones).
» Augment skeletal muscle buffering capacity, allowing you to squeeze out more sets and recover more quickly.
» Delay muscular fatigue during exercise.
» Speed recovery process after exercise.
Additionally, glutamine's positive impact on immune function ensures that chronic training won't result in having to take days off due to sickness. These benefits are especially advantageous for competitive body-builders - anything that acts as an anti-catabolic agent and fat-burner is critical to achieving your bodybuilding goals.
ON THE SAFE SIDE
Glutamine supplementation provides a number of advantages for those undergoing heavy training. Aside from all of the benefits, glutamine is also relatively safe to use as a supplement. Very few side effects are noted in the scientific literature, except at higher individual doses (more than 10 grams per serving), and even then the reports are minimal. At high doses you may experience stomach upset, diarrhea or nausea. As with most supplements each person will have a different tolerance, so start with lower doses and gradually find your optimal dose (your maximum dose with minimal side effects and greatest gains). Finally, in an effort to minimize any discomfort for which you may be susceptible, be certain to choose high-quality products from established manufacturers - you really do get what you pay for.UNDER STUDY
Volumes of research show glutamine's numerous benefits to the bodybuilder. Here are some more recent findings that substantiate glutamine as a critical supplement.In a relatively recent study, glutamine supplementation significantly increased serum growth hormone levels after only three weeks of ingestion (5 grams per day) in middle-aged subjects. These findings are a huge benefit as growth hormone regulates muscular development and reduces body-fat. Glutamine has also been shown to increase skeletal muscle glucose uptake after exercise, which means the amino acid may shorten post-workout recovery time (refueling muscle cells with sugar is critical for hard-training bodybuilders).
Scientists from Brazil recently reported in a study that glutamine ingestion increased insulin sensitivity (a supporting event for increased glucose uptake) in skeletal muscle. Furthermore, the researchers reported that glutamine ingestion decreased fat mass. This occurrence was a result of decreased insulin sensitivity in fat cells within the body.
Scientists from Iowa State University (Ames) reported that glutamine ingestion increases energy expenditure after a mixed meal. When a person's blood glutamine is elevated and then he or she eats a meal, two phases of increased energy expenditure are noted: There's an early phase that results from increased glucose uptake. Then, there's a late phase because of increased fat-burning. This data provides definitive support for glutamine's impact on balancing blood glucose levels and fat oxidation.
Scientists in the Netherlands found that glutamine ingestion results in a significant increase in plasma citrulline and arginine (most likely released from the liver and intestines). Both substrates are intimately involved in nitric-oxide (NO) production. This relatively unexplored effect of glutamine supplementation gives rise to yet another avenue, suggesting that glutamine may enhance post-exercise recovery and muscular development.